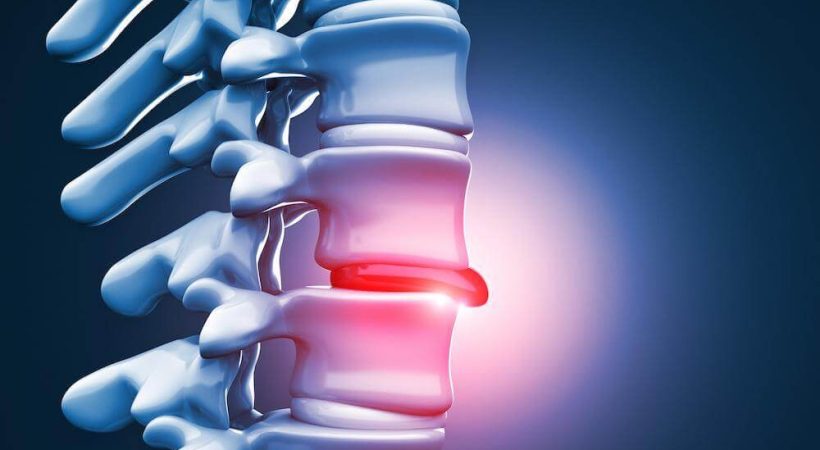
Discogenic pain refers to pain that originates from the intervertebral disc, the cushion-like structure located between two vertebrae in the spine. One common form of discogenic pain is disc herniation, which happens when the outer layer of the disc tears and the inner material protrudes, putting pressure on a nerve root. However, it’s important to note that not all cases of discogenic pain are caused by herniation. In fact, discogenic pain can occur without a visible herniation on MRI.
Other factors, such as disc degeneration, annular tears, and chemical irritation, can also contribute to discogenic pain. These factors may affect the structural integrity and function of the intervertebral disc, leading to pain and discomfort. It’s crucial to accurately diagnose the underlying cause of discogenic pain to develop an appropriate treatment plan for effective pain management and restoration of function.